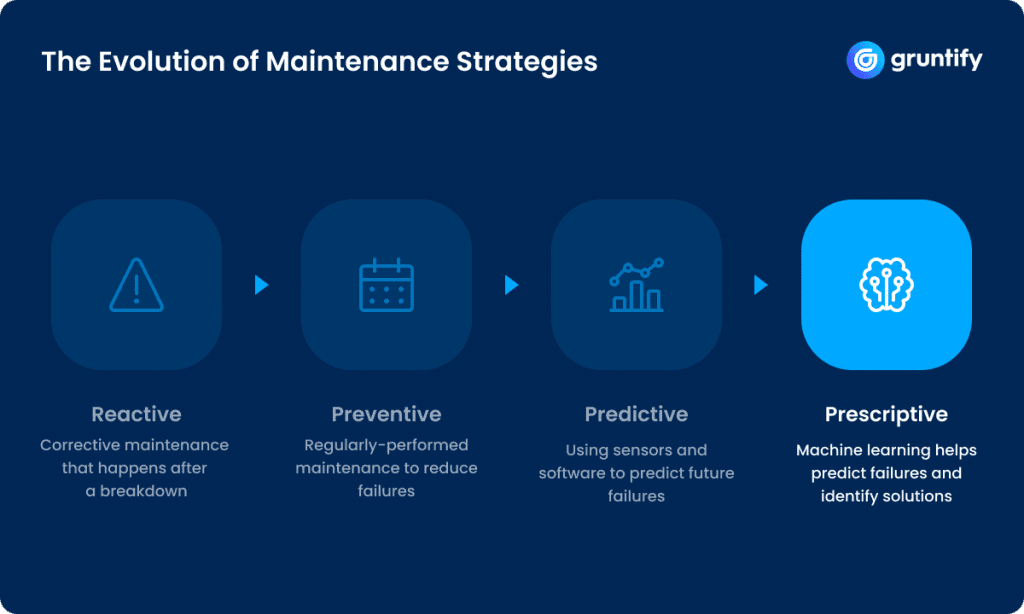
Organizations use multiple maintenance strategies to ensure the most cost-effective solution for each asset. Sometimes, companies find themselves using reactive maintenance because they’ve experienced equipment failure. Most businesses use preventative maintenance to schedule maintenance before a failure occurs. Some enterprises are also implementing predictive maintenance by deploying sensors and other IoT devices to collect data. The data delivers condition-based alerts, so maintenance personnel can take corrective action to keep assets operational.
But what if companies could take maintenance a step further? What if they could use the collected data to alert personnel of potential failures and provide solutions to fix the issues? Better yet, what if a maintenance strategy could implement the solution without human intervention? Prescriptive maintenance (RxM) can do just that. It uses prescriptive algorithms to analyze the data collected from multiple endpoints to deliver a list of possible solutions.
What is Prescriptive Maintenance?
Prescriptive maintenance uses condition monitoring data collected from IoT devices to fuel artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms. RxM ingests the same data as predictive maintenance but adds machine learning technologies to select potential outcomes and recommend the best solutions. As new data is added, the AI-based technology adjusts its processing to reflect changes in operational data accurately.
The algorithms can use the same data that predictive maintenance models use to develop a historical view of the asset. Predictive outcomes are determined, and then the prescriptive algorithms are added. With AI technologies, models continually learn and identify patterns that humans cannot detect, given the volume of data that needs processing.
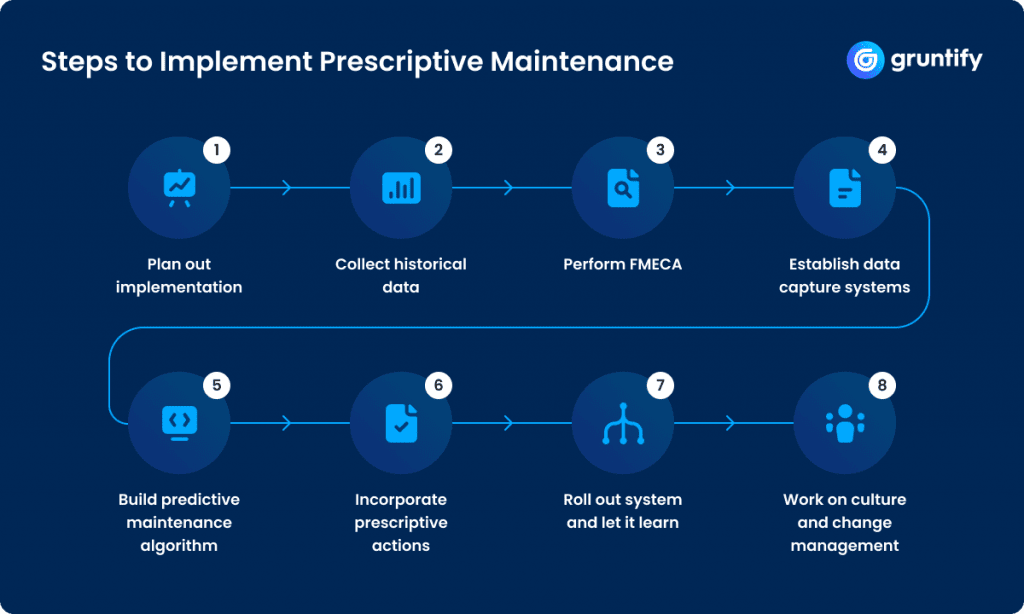
How to Implement Prescriptive Maintenance
The following prescriptive maintenance steps may be familiar for organizations using predictive maintenance; however, it’s essential to review each step for applicability to a prescriptive program.
Make a Plan
Implementing a prescriptive maintenance program takes time. Most enterprises begin with a pilot project that focuses on a critical asset. This approach limits the required data and ensures that the algorithms are functioning as expected before placing the solution in production.
Collect Data
The better the data, the better the outcome. In this step, businesses should identify the data needed for the pilot program and ensure that the information is available in digital form. For companies using predictive maintenance, the historical data should be available as part of the condition monitoring.
Failure Mode Analysis
Since the primary purpose of RxM is to understand equipment failures, organizations need to identify:
- How has the equipment failed in the past?
- What were the results of those failures?
- The risks associated with equipment failure.
- The criticality level of the failed equipment.
This analysis also forms the prescriptive base for the algorithms that the system uses to suggest solutions.
Data Capture
Condition monitoring data is part of predictive maintenance. That same real-time data from IoT devices provides the basis for prescriptive maintenance. As conditioning information is transmitted, it can be extracted, aggregated, as well as analyzed to deliver recommendations and alerts. For AI to provide the best solutions, data must be available in real-time at bandwidth and capacity to support comprehensive data analysis.
RxM Algorithms
Algorithms are mathematical equations that explain, for example, how a cooling system works. These algorithms incorporate information from the following sources to address each failure scenario:
- Manufacturer’s original documentation
- Service history
- Condition monitoring
- Personnel input
The information is used to build models that can be tested before AI solutions are added.
RxM Responses
The predictive algorithms identify failures that prescriptive AI responds to. Based on the failure mode analysis, algorithms respond to factors indicating a potential failure. For example, an elevator transmits data showing a slight rise in temperature near a pulley. Prescriptive maintenance assesses the situation, determines that a change in tension would reduce friction, as well as allows the unit to operate until its scheduled maintenance window.
RxM solutions could confirm that maintenance is scheduled and enter the pulley information into the service order. It could associate repair information and list the components that may address the problem. When the service technician pulls the order, the data ensures that the necessary tools and parts are on-hand.
Testing
Testing is also crucial to a successful prescriptive maintenance program. Initial algorithms are rarely perfect. They need to be refined to address the specific operating conditions. AI needs time to ingest the data, learn from it, as well as improve responses. Human oversight is necessary to ensure the solution is working as planned. It’s much easier to identify weaknesses when the focus is on a single item rather than an entire operation.
As testing progresses, the initial model can be analyzed to determine how well the prescribed changes address operational efficiencies. Refinements can be made. When everyone is comfortable with the implementation, the system can start with minimal human monitoring.
Change Management
Although change management is listed at the end of the process, it needs to be part of the implementation from the beginning. Using prescriptive maintenance solutions requires changes in internal processes and procedures. Service personnel may have less paperwork as the system can confirm schedules, order parts, and identify reference tools. The system could even produce compliance or regulatory documents from the servicer’s notes.
These changes can also help staff operate more efficiently, but they need appropriate training to make it happen. Having a plan to manage changes makes it easier for people to accept them, leading to a more positive outcome.
Why Prescriptive Maintenance?
Prescriptive maintenance solutions use AI technology to :
- Prescribe the best solutions for failure scenarios.
- Identify the financial implications of different corrective actions.
- Build digital models to simulate operational changes before their implementation.
- Optimize operations and increase efficiencies.
- Minimize unplanned downtime.
- Highlight unrecognized issues.
With the capacity to process volumes of data, prescriptive solutions can alert personnel to potential problems before they have a negative impact and provide the best possible response. However, implementing prescriptive maintenance does have its drawbacks.
Prescriptive maintenance may mean adding sensors and IoT devices to existing architecture, which may require network upgrades. It is an emerging technology that may require added resources for system integration. Processes and procedures will need modification, and regulatory reporting may not keep up with the technology.
Future of Prescriptive Maintenance
RxM has the potential to change the process of maintenance; however, it will take time to implement given its complexity. Like most AI solutions, prescriptive maintenance requires accurate and comprehensive data that can train the software and enable it to learn. It introduces operational changes that need clear communications to ensure acceptance. It may not be the best strategy for everyone.
Different organizations use different maintenance strategies. Many incorporate more than one approach to maintenance management. For organizations using predictive maintenance, RxM is the next step in delivering cost-effective operational efficiencies.
If you are looking to improve operational efficiencies with effective maintenance management, Gruntify’s Field Service Automation Software can help. Our solution supports multiple maintenance strategies to deliver an integrated solution that grows with you. Contact us today to learn more.

